Nikola Tesla

Nikola Tesla (July 9, 1856 - January 7, 1943) was a physicist, inventor, and electrical engineer of unusual intellectual brilliance and practical achievement. He was of Serb descent and worked mostly in the United States.
Tesla is most famous for conceiving the rotating magnetic field principle (1882) and then using it to invent the induction motor together with the accompanying alternating current long-distance electrical transmission system (1888). His patents and theoretical work still form the basis for modern alternating current electric power systems.
He also developed numerous other electrical and mechanical devices including the fundamental principles and machinery of wireless technology, including the high frequency alternator, the "AND" logic gate and the Tesla coil, as well as other devices such as the bladeless turbine, the spark plug and numerous other inventions.
Tesla was born to a Serbian family in the village of Smiljan near Gospic, in the Lika region in Krajina, Croatia (then part of the Austrian Empire). According to legend, he was born precisely at midnight during an electrical storm.
His father was Rev. Milutin Tesla, a priest in the Serbian Orthodox Church Metropolitanate of Sremski Karlovci. Milutin was born on 19 February 1819 in the village of Meduc, county Medak in Lika, Austrian Empire, as son of Nikola Tesla (b. 1789 in the military frontier, settled after his service in the Napoleonic Wars in Gospic in 1815) and Ana Kalinic, from the famous frontier Kalinic family. Tesla's family asserted its last name as such in Lika. His paternal origin is thought to be of the Draganic family from the Tara valley area below the geographical entity known as Old Vlach, from one of the local Serb clans; however genealogical research shows that Nikola is from the Herzegovinian noble Komnenovic (modern-day Old Herzegovina in Montenegro), from its Orlovic subgroup that traces its origin from the semi-mythic Pavle Orlovic that bore Prince Lazar's banner at the Battle of Kosovo in 1389. His mother was Duka Mandic, herself a daughter of a Serbian Orthodox Church priest. She came from a family domiciled in Lika and Banija, but with deeper origins to Kosovo. She was talented in making home craft tools. She memorized many Serbian epic poems, but never learned to read. His godfather, Jovan Drenovac, was a captain in the army protecting the Military Frontier.
Nikola was one of five children, having one brother (Dane, who was killed in a horse-riding accident when Nikola was five) and three sisters (Milka, Angelina and Marica). His family moved to Gospic in 1862. Tesla went to school in Karlovac. He finished a four year term in the span of three years.
Tesla then studied electrical engineering at the Austrian Polytechnic in Graz (1875). While there, he studied the uses of alternating current. Some sources say he received Baccalaureate degrees from the university at Graz. However, the university says that he did not receive a degree and did not continue beyond the first semester of his third year, during which he stopped attending lectures. In December 1878 he left Graz and broke all relations with his family. His friends thought that he had drowned in Mura. He went to Maribor, Slovenia, where he was first employed as an assistant engineer for a year. He suffered a nervous breakdown during this time. Tesla was later persuaded by his father to attend the Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague, which he attended for the summer term of 1880. Here he was influenced by Ernst Mach. However after his father died he left the university, having completed only one term.
Tesla engaged in reading many works, memorizing complete books, supposedly having a photographic memory. Tesla related in his autobiography that he experienced detailed moments of inspiration. During his early life, Tesla was stricken with illness time and time again. He suffered a peculiar affliction in which blinding flashes of light would appear before his eyes, often accompanied by hallucinations. Much of the time the visions were linked to a word or idea he might have come across; just by hearing the name of an item, he would involuntarily envision it in realistic detail. Modern-day synesthetes report similar symptoms. Tesla would visualise an invention in his brain in precise form before moving to the construction stage; a technique sometimes known as picture thinking. Tesla also often had flashbacks to events that had happened previously in his life; this began to happen during childhood.
Hungary and France
In 1881, he moved to Budapest, Hungary, to work under Tivadar Puskas in a telegraph company,the National Telephone Company. There, he met Nebojsa Petrovic, a young inventor from Austria. Although their encounter was brief, they did work on a project together using twin turbines to create continual power. On the opening of the telephone exchange in Budapest, 1881, Tesla became the chief electrician to the company, and was later engineer for the country's first telephone system. He also developed a device that, according to some, was a telephone repeater or amplifier, but according to others could have been the first loudspeaker.
In 1882 he moved to Paris, France, to work as an engineer for the Continental Edison Company, designing improvements to electric equipment. In the same year, Tesla conceived the induction motor and began developing various devices that use rotating magnetic fields (for which he received patents in 1888).
Soon thereafter, Tesla hastened from Paris to his mother's side as she lay dying, arriving hours before her death in April, 1892. Her last words to him were, "You've arrived, Nidzo, my pride." After her death, Tesla fell ill. He spent two to three weeks recuperating in Gospic and the village of Tomingaj near Gracac, the birthplace of his mother.
On June 6, 1884, Tesla first arrived in the US in New York City. He had little besides a letter of recommendation from Charles Batchelor, his manager in his previous job. In the letter of recommendation to Thomas Edison, Charles Batchelor wrote, "I know two great men and you are one of them; the other is this young man." Edison hired Tesla to work for his company Edison Machine Works. Tesla's work for Edison began with simple electrical engineering and quickly progressed to solving the company's most difficult problems. Tesla was offered the task of a complete redesign of the Edison company's direct current generators.
During his employment, Tesla claims Edison offered him $50,000 (equivalent to about $1 million in 2006, adjusted for inflation if he redesigned Edison's inefficient motor and generators, an improvement in both service and economy.
Tesla said he worked night and day to redesign them and gave the Edison company several profitable new patents in the process. During the year of 1885, when Tesla inquired about the payment on the work, Edison replied to him, "Tesla, you don't understand our American humor," and reneged on his promise. This anecdote is somewhat doubtful, since at Tesla's salary of $18 per week the bonus would have amounted to over 53 years pay, and the amount was equal to the initial capital of the company.Tesla resigned when he was refused a raise to $25 per week.
Tesla eventually found himself digging ditches for a short period of time - coincidentally for the Edison company. Edison had also never wanted to hear about Tesla's AC polyphase designs, believing that DC electricity was the future. Tesla focused intently on his AC polyphase system, even while digging ditches.
In 1886, Tesla formed his own company, Tesla Electric Light & Manufacturing. The initial financial investors disagreed with Tesla on his plan for an alternating current motor and eventually relieved him of his duties at the company. Tesla worked in New York as a common laborer from 1886 to 1887 to feed himself and raise capital for his next project.
In 1887, he constructed the initial brushless alternating current induction motor, which he demonstrated to the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (now IEEE) in 1888. In the same year, he developed the principles of his Tesla coil and began working with George Westinghouse at Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company's Pittsburgh labs. Westinghouse listened to his ideas for polyphase systems which would allow transmission of alternating current electricity over large distances.
In April of 1887, Tesla began investigating what would later be called X-rays using his own single node vacuum tubes (similar to his patent #514,170 ). This device differed from other early X-ray tubes in that they had no target electrode. The modern term for the phenomenon produced by this device is bremsstrahlung (or braking radiation). We now know that this device operated by emitting electrons from the single electrode through a combination of field emission and thermionic emission. Once liberated, electrons are strongly repelled by the high electric field near the electrode during negative voltage peaks from the oscillating HV output of the Tesla Coil, generating X-rays as they collide with the glass envelope. He also used Geissler tubes. By 1892, Tesla became aware of what Wilhelm Röntgen later identified as effects of X-rays.
In the early research, Tesla devised several experimental setups to produce X-rays. Tesla held that, with his circuits, the "instrument will [... enable one to] generate Roentgen rays of much greater power than obtainable with ordinary apparatus." He also commented on the hazards of working with his circuit and single node X-ray producing devices. Of his many notes in the early investigation of this phenomenon, he attributed the skin damage to various causes. One of the options for the cause, which is not in conformity with conventional x-ray production, was that the ozone generated rather than the radiation was responsible.
Tesla continued research in the field and, later, observed an assistant severely "burnt" by X-rays in his lab. He performed several experiments prior to Roentgen's discovery (including photographing the bones of his hand; later, he sent these images to Roentgen) but didn't make his findings widely known; much of his research was lost in the 5th Avenue lab fire of March 1895.
A "world system" for "the transmission of electrical energy without wires" that depends upon the electrical conductivity was proposed in which transmission in various natural mediums with current that passes between the two point are used to power devices. In a practical wireless energy transmission system using this principle, a high-power ultraviolet beam might be used to form a vertical ionized channel in the air directly above the transmitter-receiver stations. The same concept is used in virtual lightning rods, the electrolaser electroshock weapon, and has been proposed for disabling vehicles.
Tesla demonstrated "the transmission of electrical energy without wires" that depends upon electrical conductivity as early as 1891. The Tesla effect (named in honor of Tesla) is the archaic term for an application of this type of electrical conduction (that is, the movement of energy through space and matter; not just the production of voltage across a conductor).
On July 30, 1891, he became a naturalized citizen of the United States at the age of 35. Tesla established his 35 South Fifth Avenue laboratory in New York during this same year. Later, Tesla would establish his Houston Street laboratory in New York at 46 E. Houston Street. There, at one point while conducting mechanical resonance experiments with electro-mechanical oscillators he generated a resonance of several surrounding buildings but, due to the frequencies involved, not his own building, causing complaints to the police.
As the speed grew he hit the resonant frequency of his own building and belatedly realizing the danger he was forced to apply a sledge hammer to terminate the experiment, just as the astonished police arrived. He also lit vacuum tubes wirelessly at both of the New York locations, providing evidence for the potential of wireless power transmission. Some of Tesla's closest friends were artists. He befriended Century Magazine editor Robert Underwood Johnson, who adapted several Serbian poems of Jovan Jovanovic Zmaj (which Tesla translated). Also during this time, Tesla was influenced by the Vedic philosophy teachings of the Swami Vivekananda.
When Tesla was 36 years old, the first patents concerning the polyphase power system were granted. He continued research of the system and rotating magnetic field principles. Tesla served, from 1892 to 1894, as the vice president of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, the forerunner (along with the Institute of Radio Engineers) of the modern-day IEEE.
From 1893 to 1895, he investigated high frequency alternating currents. He generated AC of one million volts using a conical Tesla coil and investigated the skin effect in conductors, designed tuned circuits, invented a machine for inducing sleep, cordless gas discharge lamps, and transmitted electromagnetic energy without wires, building the first radio transmitter. In St. Louis, Missouri, Tesla made a demonstration related to radio communication in 1893. Addressing the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and the National Electric Light Association, he described and demonstrated in detail its principles. Tesla's demonstrations were written about widely through various media outlets. Tesla also investigated harvesting energy that is present throughout space. He believed that it was just merely a question of time when men will succeed in attaching their machinery to the very wheelwork of nature.
At the 1893 World's Fair, the World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago, an international exposition was held which for the first time devoted a building to electrical exhibits. It was an historic event as Tesla and George Westinghouse introduced visitors to AC power by using it to illuminate the Exposition. On display were Tesla's fluorescent lamps and single node bulbs.
Tesla also explained the principles of the rotating magnetic field and induction motor by demonstrating how to make an egg made of copper stand on end in his demonstration of the device he constructed known as the "Egg of Columbus".
Also in the late 1880s, Tesla and Edison became adversaries in part due to Edison's promotion of direct current (DC) for electric power distribution over the more efficient alternating current advocated by Tesla and Westinghouse. Until Tesla invented the induction motor, AC's advantages for long distance high voltage transmission were counterbalanced by the inability to operate motors on AC. As a result of the "War of Currents," Edison and Westinghouse went nearly bankrupt, so in 1897, Tesla released Westinghouse from contract, providing Westinghouse a break from Tesla's patent royalties. Also in 1897, Tesla researched radiation which led to setting up the basic formulation of cosmic rays.
When Tesla was forty-one years old, he filed the first basic radio patent (U.S. Patent 645,576 ). A year later, he demonstrated a radio controlled boat to the US military, believing that the military would want things such as radio controlled torpedoes. Tesla had developed the "Art of Telautomatics", a form of robotics, as well as the technology of remote control.
In 1898, a radio-controlled boat was demonstrated to the public during an electrical exhibition at Madison Square Garden. These devices had an innovative coherer and a series of logic gates. Tesla called his boat a "teleautomaton" and said of it, "You see there the first of a race of robots, mechanical men which will do the laborious work of the human race."
Radio remote control remained a novelty until the 1960s. In the same year, Tesla devised an "electric igniter" or spark plug for Internal combustion gasoline engines. He gained U.S. Patent 609,250 , "Electrical Igniter for Gas Engines", on this mechanical ignition system. Tesla lived in the former Gerlach Hotel, renamed The Radio Wave building, at 49 W 27th St. (between Broadway and Sixth Avenue), Lower Manhattan, before the end of the century where he conducted the radio wave experiments. A commemorative plaque was placed on the building in 1977 to honor his work.
Wireless and the AIEE

Tesla served as the Vice-President of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (now part of the IEEE) from 1892 to 1894. From 1893 to 1895, he investigated high frequency alternating currents. He generated AC of one million volts using a conical Tesla coil and investigated the skin effect in conductors, designed tuned circuits, invented a machine for inducing sleep, cordless gas discharge lamps, and transmitted electromagnetic energy without wires, effectively building the first radio transmitter.
In St. Louis, Missouri, Tesla made a demonstration related to radio communication (he demonstrated radio energy crossing space (one side of a stage to the other) in 1893. Addressing the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and the National Electric Light Association, he described and demonstrated in detail its principles. Heinrich Hertz had made such demonstrations, repeatedly, five years previously. Hertz' demonstrations were not public (they were conducted during his physics lectures) but strictly speaking neither were Tesla's (the Franklin Institute didn't open to the general public until 1934).
Tesla held over forty U.S. patents (circa 1888) covering our entire system of Polyphase Alternating Current (AC). These patents are so novel that nobody could ever challenge them in the courts.
Tesla's four-tuned circuits (two on the receiving side and two on the transmitting side, secured by U.S. patents #645,576 and #649,621) were the basis of the U.S. Supreme Court decision (Case #369 decided June 21, 1943) to overturn Marconi's basic patent on the invention of radio.
World's Fair Exposition
At the 1893 World's Fair, the World Columbian Exposition in Chicago, Illinois, an international exposition was held which for the first time devoted a building to electrical exhibits. It was a historic event as Tesla and George Westinghouse introduced visitors to AC power by using it to illuminate the Exposition. In protest, Edison would not allow use of any of his lightbulbs for this event.
As if lighting the Exposition was not enough, Tesla explained the principles of the rotating magnetic field and induction motor by demonstrating how to make an egg (made of copper) stand on end in his version of the Egg of Columbus.
War of currents
In the "War of Currents" era in the late 1880s, Nikola Tesla and Thomas Edison became adversaries due to Edison's promotion of direct current (DC) for electric power distribution over the more efficient alternating current (AC) advocated by Tesla.
1896-1899
When Tesla was 41 years old, he filed the first basic radio patent (No. US645576). A year later, he demonstrated a remote controlled boat to the US military, believing that the military would want things such as radio-guided torpedoes. In 1898 a radio controlled boat was also demonstrated to the public during an electrical exhibition at Madison Square Garden. These devices had an innovative coherer and a series of logic gates. Radio remote control remained a novelty until the Space Age. In the same year, Tesla devised an electric igniter for gasoline engines which was nearly identical to ideas about the same process used by modern internal combustion engines.
In 1896, according to an interview he gave in 1916, Tesla invented a type of loudspeaker. The sounds were of the quality of the telephones of that time. The invention was never patented nor released publicly (till years later by Tesla himself).
As a result of the "War of Currents" Edison and Westinghouse were almost bankrupt, so in 1897 Tesla released Westinghouse from contract providing Westinghouse a break from Tesla's AC motor royalties.
Colorado Springs
In 1899, Tesla decided to move and began research in Colorado Springs, Colorado, where he could have room for his high-voltage high-frequency experiments. He chose this location primarily because of the frequent thunderstorms, the high altitude (where the air, being at a lower pressure, had a lower dielectric breakdown strength, making it easier to ionize), and the dryness of the air (minimizing leakage of electric charge through insulators). Also, the property was free and electric power available from the El Paso Power Company. Today, magnetic intensity charts also show that the ground around his lab possesses a denser magnetic field than the surrounding area. Tesla reached Colorado Springs on May 17, 1899. Upon his arrival he told reporters that he was conducting experiments transmitting signals from Pikes Peak to Paris.
Tesla kept a diary of his experiments in the Colorado Springs lab where he spent nearly nine months. It consists of 500 pages of handwritten notes and nearly 200 drawings, recorded chronologically between June 1, 1899 and January 7, 1900, as the work occurred, containing explanations of his experiments. He was developing a system for wireless telegraphy, telephony and the transmission of power, experimented with high-voltage electricity and the possibility of wireless transmitting and distributing large amounts of electrical energy over long distances. He also conceived a system for geophysical exploration--seismology--which he called telegeodynamics, based on his reciprocating mechanical oscillator patented in 1894, and explained that a long sequence of small explosions could be used to find ore and create earthquakes large enough to destroy the Earth. He did not experiment with this as he felt there would not be "a desirable outcome".
Much of what Tesla discovered while in this lab has been lost to history and Tesla's own secrecy. To this very day there is talk of Tesla's Death Ray being invented there as well as communication with other planets. How much of this is true is now unknown, but has made Tesla's time at this remote lab a wellspring for Urban legends about him.
Laboratory construction
Tesla, a local contractor, and several assistants commenced the construction of the laboratory shortly after arriving in Colorado Springs. The lab was established on Knob Hill, east of the Colorado School for the Deaf and Blind and one mile (1.6 km) east of downtown. Its primary purposes were experiments with high frequency electricity and other phenomena, and secondary--research into wireless transmission of electrical power.
Tesla's design of the lab was a building fifty feet by sixty feet (15 by 18 m) with eighty-foot (24 m) ceilings. A one-hundred-forty-two foot (43 m) conducting aerial with a thirty-inch (760 mm) copper-foil-covered wooden ball was erected on the roof. The roof was rolled back to prevent fire from sparks and other dangerous effects of the experiments. The laboratory had sensitive instruments and equipment.
Magnifying transmitter
Missing imageTesla_colorado_444px.jpgDouble exposure publicity photo of Tesla sitting in his laboratory in Colorado Springs with his "magnifying transmitter" generating millions of volts of electricity. The arcs are about 22 feet (7 m) long.
The lab possessed the largest Tesla Coil ever built, fifty-two feet (16 m) in diameter, known as the Magnifying Transmitter (further MT). Not identical to a classic Tesla Coil, it was a three-coil magnifying system requiring different forms of analysis than lumped-constant coupled resonant coils presently described to most. It resonated at a natural quarter wavelength frequency and could work in a continuous-wave mode and in a partially damped-wave resonant mode.
According to accounts, Tesla used it to transmit tens of thousands of watts of power wirelessly; it could generate millions of volts of electricity and produce lightning bolts more than one-hundred feet (30 m) long. Tesla posted a large fence around it with a sign "Keep Out - Great Danger".
Tesla became the first man to create electrical effects on the scale of lightning. The MT produced thunder which was heard as far away as Cripple Creek. People near the lab would observe sparks emitting from the ground to their feet and through their shoes. Some have observed electrical sparks from the fire hydrants (Tesla for a time grounded out to the plumbing of the city). The area around the laboratory would glow with a blue corona (similar to St. Elmo's Fire).
One of Tesla's experiments with the MT destroyed Colorado Springs Electric Company's generator by backfeeding the city's power generators, and blacked out the city. The company denied Tesla further access to the backup generator's feed if he did not repair the primary generator at his own expense; it was working again in a few days.
Tuned circuits
Tesla also constructed many smaller resonance transformers and discovered the concept of tuned electrical circuits. He also developed a number of coherers for separating and perceiving electromagnetic waves and designed rotating coherers which he used to detect the unique types of electromagnetic phenomenon he observed. They had a mechanism of geared wheels driven by a coiled spring-drive mechanism which rotated small glass cylinders. These experiments were the final stage of years of work on synchronized tuned electrical circuits.
These transceivers were constructed to demonstrate how signals could be "tuned in". Tesla logged in his diary on July 3, 1899 that a separate resonance transformer tuned to the same high frequency as a larger high-voltage resonance transformer would transceive energy from the larger coil, acting as a transmitter of wireless energy, which was used to confirm Tesla's patent for radio during later disputes in the courts. These air core high-frequency resonate coils were the predecessors of systems from radio to radar and medical magnetic resonance imaging devices.
Propagation and resonance
On July 3, 1899, Tesla discovered terrestrial stationary waves within the earth. He demonstrated that the Earth behaves as a smooth polished conductor and possesses electrical vibrations. He experimented with waves characterized by a lack of vibration at points, between which areas of maximum vibration occur periodically. These standing waves were produced by confining waves within constructed conductive boundaries. Tesla demonstrated that the Earth could respond at predescribed frequencies of electrical vibrations. At this time, Tesla realized that it was possible to transceive power around the globe. A few years later, George Westinghouse stopped funding Tesla's research when Tesla showed him that he could offer free electricity to the whole world by simply "ramming a stick in the earth in your backyard". Westinghouse said he would go bankrupt if that happened.
Tesla conducted experiments contributing to the understanding of electromagnetic propagation and the Earth's resonance. It is well documented (from various photos from the time) that he lit hundreds of lamps wirelessly at a distance of up to twenty-five miles (40 km). He transmitted signals several kilometres and lit neon tubes conducting through the ground. He researched ways to transmit energy wirelessly over long distances. He transmitted extremely low frequencies through the ground in his experiments and made mathematical calculations and computations based on his experiments and discovered that the resonant frequency of the Earth was approximately 8 Hz (Hertz). In the 1950s, researchers confirmed resonant frequency was in this range (interesting to note, Theta brain waves also cycle in this range).
Cosmic waves
In the Colorado Springs lab, Tesla recorded what he concluded were extraterrestrial radio signals and announced his findings in some of the scientific journals of the time. [5] His announcements and data were rejected by the scientific community who did not believe him. He notes measurements of repetitive signals from his receiver which are substantially different from the signals he had noted from storms and earth noise. Specifically, he later recalled that the signals appeared in groups of clicks 1, 2, 3, and 4 clicks together. He stated in the article "A Giant Eye to See Round the World", of February 25, 1923, that:
- "Twenty-two years ago, while experimenting in Colorado with a wireless power plant, I obtained extraordinary experimental evidence of the existence of life on Mars. I had perfected a wireless receiver of extraordinary sensitiveness, far beyond anything known, and I caught signals which I interpreted as meaning 1--2--3--4. I believe the Martians used numbers for communication because numbers are universal."
Clearly, Tesla felt the signal groups originated on the planet Mars. In 1996 Corum and Corum published an analysis of Jovian plasma torus signals which indicate that there was a correspondence between the setting of Mars at Colorado Springs, and the cessation of signals from Jupiter in the summer of 1899 when Tesla was there. Further, analysis by the Corums indicate that Tesla's transceiver was sensitive in the 18 kHz gap in the Kennelly-Heaviside layer which would have allowed that reception from Jupiter. Therefore, there is evidence the signals Tesla noticed came from Jupiter, among other possible sources. Tesla spent the latter part of his life trying to signal Mars.
It is important to recognize that when he says he "recorded" these signals, it is meant that he wrote down the data and his impressions of what he had heard. He did release reports at the time. Tesla¹s initial announcement of the existence of extraterrestrial radio signals was in 1899. In March of 1907, Tesla wrote about signaling to Mars in Harvard Magazine and how it was a problem of electrical engineering. Additional descriptions come from remembrances twenty years later. All this was met with resistance and disbelief by his contemporaries.
Colorado Departure
Tesla left Colorado Springs on January 7, 1900. The lab was torn down, broken up, and its contents sold to pay debts. The Colorado experiments prepared Tesla for his next project, the establishment of a wireless power transmission facility that would be known as Wardenclyffe. On March 21, 1900, Tesla was granted US685012 patent for the means for increasing the intensity of electrical oscillations.
In 1900, with $150,000 (51 % from J. Pierpont Morgan), Tesla began planning the Wardenclyffe Tower facility. In June 1902, Tesla's lab operations were moved to Wardenclyffe from Houston Street. The tower was finally dismantled for scrap during World War I. Newspapers of the time labeled Wardenclyffe "Tesla's million-dollar folly." In 1904, the US Patent Office reversed its decision and awarded Guglielmo Marconi the patent for radio, and Tesla began his fight to re-acquire the radio patent. On his 50th birthday in 1906, Tesla demonstrated his 200 hp (150 kW) 16,000 rpm bladeless turbine. During 19101911 at the Waterside Power Station in New York, several of his bladeless turbine engines were tested at 1005000 hp.
Since the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Marconi for radio in 1909, Thomas Edison and Tesla were mentioned as potential laureates to share the Nobel Prize of 1915 in a press dispatch, leading to one of several Nobel Prize controversies. Some sources have claimed that due to their animosity toward each other neither was given the award, despite their enormous scientific contributions, and that each sought to minimize the other one's achievements and right to win the award, that both refused to ever accept the award if the other received it first, and that both rejected any possibility of sharing it.
In the following events after the rumors, neither Tesla nor Edison won the prize (although Edison did receive one of 38 possible bids in 1915, and Tesla did receive one bid out of 38 in 1937).
Earlier, Tesla alone was rumored to have been nominated for the Nobel Prize of 1912. The rumored nomination was primarily for his experiments with tuned circuits using high-voltage high-frequency resonant transformers.
In 1915, Tesla filed a lawsuit against Marconi attempting, unsuccessfully, to obtain a court injunction against the claims of Marconi. After Wardenclyffe, Tesla built the Telefunken Wireless Station in Sayville, Long Island. Some of what he wanted to achieve at Wardenclyffe was accomplished with the Telefunken Wireless. In 1917, the facility was seized and torn down by the Marines, because it was suspected that it could be used by German spies.
Prior to World War I, Tesla looked overseas for investors to fund his research. When the war started, Tesla lost the funding he was receiving from his European patents. After the war ended, Tesla made predictions regarding the relevant issues of the post-World War I environment, in a printed article (December 20, 1914).
Tesla believed that the League of Nations was not a remedy for the times and issues. Tesla started to exhibit pronounced symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the years following. He became obsessed with the number three; he often felt compelled to walk around a block three times before entering a building, demanded a stack of three folded cloth napkins beside his plate at every meal, etc. The nature of OCD was little understood at the time and no treatments were available, so his symptoms were considered by some to be evidence of partial insanity, and this undoubtedly hurt what was left of his reputation.
At this time, he was staying at the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel, renting in an arrangement for deferred payments. Eventually, the Wardenclyffe deed was turned over to George Boldt, proprietor of the Waldorf-Astoria to pay a $20,000 debt. In 1917, around the time that the Wardenclyffe Tower was demolished by Boldt to make the land a more viable real estate asset, Tesla received AIEE's highest honor, the Edison Medal.
Tesla, in August 1917, first established principles regarding frequency and power level for the first primitive RADAR units.
In 1934, Emile Girardeau, working with the first French RADAR systems, stated he was building RADAR systems "conceived according to the principles stated by Tesla". By the twenties, Tesla was reportedly negotiating with the United Kingdom government about a ray system. Tesla had also stated that efforts had been made to steal the so called "death ray". It is suggested that the removal of the Chamberlain government ended negotiations.
On Tesla's seventy-fifth birthday in 1931, Time magazine put him on its cover. The cover caption noted his contribution to electrical power generation. Tesla received his last patent in 1928 for an apparatus for aerial transportation which was the first instance of VTOL aircraft. By the end of 1931, Tesla released "On Future Motive Power" which covered an ocean thermal energy conversion system.
In 1934, Tesla wrote to consul Jankovic of his homeland. The letter contained the message of gratitude to Mihajlo Pupin who initiated a donation scheme by which American companies could support Tesla. Tesla refused the assistance, and chose to live by a modest pension received from Yugoslavia and to continue researching.
In 1936, Tesla stated "I'm equally proud of my Serbian origin and my Croatian homeland."
When he was eighty-one, Tesla stated he had completed a dynamic theory of gravity. He stated that it was "worked out in all details" and that he hoped to soon give it to the world. The theory was never published. At the time of his announcement, it was considered by the scientific establishment to exceed the bounds of reason. Some believe that Tesla never fully developed the Unified Field Theory.
The bulk of the theory was developed between 1892 and 1894, during the period that he was conducting experiments with high frequency and high potential electromagnetism and patenting devices for their utilization. It was completed, according to Tesla, by the end of the 1930s. Tesla's theory explained gravity using electrodynamics consisting of transverse waves (to a lesser extent) and longitudinal waves (for the majority). Reminiscent of Mach's principle.
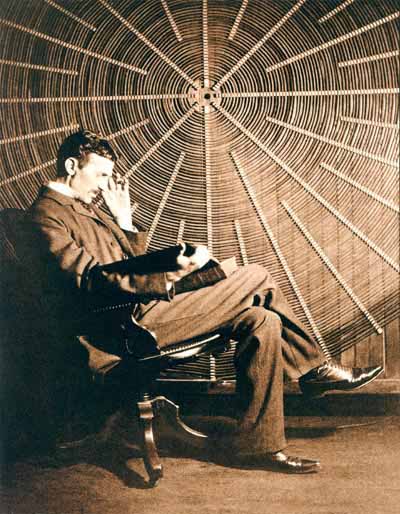

Nikola Tesla, with Ruder Boskovic's book Theoria Philosophiae Naturalis, sits in front of the spiral coil of his high-frequency transformer at East Houston Street, New York.
Later in life, Tesla made some remarkable claims concerning a "teleforce" weapon. The press called it a "peace ray" or death ray.

In total, the components and methods included:
Tesla worked on plans for a directed-energy weapon between the early 1900s till the time of his death. In 1937, Tesla composed a treatise entitled "The Art of Projecting Concentrated Non-dispersive Energy through the Natural Media" concerning charged particle beams. Tesla published the document in an attempt to expound on the technical description of a "superweapon that would put an end to all war". This treatise of the particle beam is currently in the Nikola Tesla Museum archive in Belgrade. It described an open ended vacuum tube with a gas jet seal that allowed particles to exit, a method of charging particles to millions of volts, and a method of creating and directing nondispersive particle streams (through electrostatic repulsion).
Records of his indicate that it was based on a narrow stream of atomic clusters of liquid mercury or tungsten accelerated via high voltage (by means akin to his magnifying transformer). Tesla gave the following description concerning the particle gun's operation:
- [The nozzle would] send concentrated beams of particles through the free air, of such tremendous energy that they will bring down a fleet of 10,000 enemy airplanes at a distance of 200 miles from a defending nation's border and will cause armies to drop dead in their tracks.
The weapon could be used against ground based infantry or for antiaircraft purposes. Tesla tried to interest the US War Department in the device. He also offered this invention to European countries. None of the governments purchased a contract to build the device. He was unable to act on his plans.
Tesla began to theorize about electricity and magnetism's power to warp, or rather change, space and time and the procedure by which man could forcibly control this power. Near the end of his life, Tesla was fascinated with the idea of light as both a particle and a wave, a fundamental proposition already incorporated into quantum physics.
This field of inquiry led to the idea of creating a "wall of light" by manipulating electromagnetic waves in a certain pattern. This mysterious wall of light would enable time, space, gravity and matter to be altered at will, and engendered an array of Tesla proposals that seem to leap straight out of science fiction, including anti-gravity airships, teleportation, and time travel.
The single strangest invention Tesla ever proposed was probably the "thought photography" machine. He reasoned that a thought formed in the mind created a corresponding image in the retina, and the electrical data of this neural transmission could be read and recorded in a machine. The stored information could then be processed through an artificial optic nerve and played back as visual patterns on a viewscreen.

Another of Tesla's theorized inventions is commonly referred to as Tesla's Flying Machine, which appears to resemble an ion-propelled aircraft. Tesla claimed that one of his life goals was to create a flying machine that would run without the use of an airplane engine, wings, ailerons, propellers, or an onboard fuel source. Initially, Tesla pondered about the idea of a flying craft that would fly using an electric motor powered by grounded base stations. As time progressed, Tesla suggested that perhaps such an aircraft could be run entirely electro-mechanically. The theorized appearance would typically take the form of a cigar or saucer.
Tesla died of heart failure alone in Room 3327 of the New Yorker Hotel, some time between the evening of January 5 and the morning of January 8, 1943, at the age of 86.[90] Despite selling his AC electricity patents, Tesla was destitute and died with significant debts. Later that year the US Supreme Court upheld Tesla's patent number U.S. Patent 645,576 in effect recognizing him as the inventor of radio.
Immediately after Tesla's death became known, the Federal Bureau of Investigation instructed the government's Alien Property Custodian office to take possession of his papers and property, despite his US citizenship. His safe at the hotel was also opened.
At the time of his death, Tesla had been continuing work on the teleforce weapon, or death ray, that he had unsuccessfully marketed to the US War Department. It appears that his proposed death ray was related to his research into ball lightning and plasma and was imagined as a particle beam weapon.
The US government did not find a prototype of the device in the safe. After the FBI was contacted by the War Department, his papers were declared to be top secret. The so-called "peace ray" constitutes a part of some conspiracy theories as a means of destruction. The personal effects were seized on the advice of presidential advisers, and J. Edgar Hoover declared the case "most secret", because of the nature of Tesla's inventions and patents. One document states that "[he] is reported to have some 80 trunks in different places containing transcripts and plans having to do with his experiments". Charlotte Muzar reported that there were several "missing" papers and property.
Tesla did not like to pose for portraits. He did it only once for princess Vilma Lwoff-Parlaghy. His wish was to have a sculpture made by his close friend Ivan Mestrovic, who was at that time in United States, but he died before getting a chance to see it. Mestrovic made a bronze bust (1952) that is held in the Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade and a statue (1955/56) placed at the Ruder Boskovic Institute in Zagreb. This statue was moved to Nikola Tesla Street in Zagreb's city centre on the 150th anniversary of Tesla's birth, with the Ruder Boskovic Institute to receive a duplicate. In 1976, a bronze statue of Tesla was placed at Niagara Falls, New York. A similar statue was also erected in his hometown of Gospic in 1986.
The SI unit tesla (T) for measuring magnetic flux density or magnetic induction (commonly known as the magnetic field ) was named in Tesla¹s honour at the Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures, Paris in 1960.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) of which Tesla had been vice president also created an award in recognition of Tesla. Called the IEEE Nikola Tesla Award, it is given to individuals or a team that has made outstanding contributions to the generation or utilization of electric power, and is considered the most prestigious award in the area of electric power.
The Tesla crater on the far side of the Moon and the minor planet 2244 Tesla are also named after him.
Nikola Tesla Wikipedia
 Nikola Tesla Google Videos
Nikola Tesla Google Videos

"There manifests itself in the fully developed being, Man, a desire mysterious, inscrutable and irresistible: to imitate nature, to create, to work himself the wonders he perceives. Long ago he recognized that all perceptible matter comes from a primary substance, or tenuity beyond conception, filling all space, the Akasa or luminiferous ether, which is acted upon by the life giving Prana or creative force, calling into existence, in never ending cycles all things and phenomena. The primary substance, thrown into infintesimal whirls of prodigious velocity, becomes gross matter; the force subsiding, the motion ceases and matter disappears, reverting to the primary substance." - Man's Greatest Achievement, 1907
"So astounding are the facts in this connection, that it would seem as though the Creator, himself had electrically designed this planet." - Tesla describing what is now known as Schumann Resonance (7.8Hz) in The Transmission of Electrical Energy Without Wires As A Means Of Furthering World Peace 1905.
"Of all the frictional resistances, the one that most retards human movement is ignorance, what Buddha called 'the greatest evil in the world.' The friction which results from ignorance can be reduced only by the spread of knowledge and the unification of the heterogeneous elements of humanity. No effort could be better spent."
"Science is but a perversion of itself unless it has as its ultimate goal the betterment of humanity."
